What Imaging Can You Not Do on a Baby
Pediatric MRI
Children's magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses a powerful magnetic field, radio waves and a computer to produce detailed pictures of the within of your child's body. MRI may be used to help diagnose or monitor treatment for a diversity of conditions within the brain, chest, abdomen, pelvis and extremities.
Tell your md about your kid'due south health problems, medications, recent surgeries and allergies. The magnetic field is not harmful, only it may cause some medical devices to malfunction. Most orthopedic implants pose no adventure, but you should ever tell the technologist if your child has any implanted medical or electronic devices. Inform your doctor and the technologist prior to the exam if your child has a known allergy to contrast fabric. Your child should wear loose, comfortable clothing and may exist asked to wear a gown. You may be instructed to withhold food or potable beforehand, especially if anesthesia is to be used. In general, children who accept recently been ill will not be given anesthesia. If this is the case, or if you suspect your child may be getting ill, talk to your physician about rescheduling the exam.
- What is pediatric MRI?
- What are some common uses of the procedure?
- How should I prepare my kid for the MRI?
- What does the MRI equipment await similar?
- How does the procedure work?
- How is the procedure performed?
- What will my child experience during and after the process?
- Who interprets the results and how do we become them?
- What are the benefits vs. risks?
- What are the limitations of Pediatric MRI?
What is pediatric MRI?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a noninvasive test doctors use to diagnose medical conditions.
MRI uses a powerful magnetic field, radiofrequency pulses, and a computer to produce detailed pictures of internal body structures. MRI does not employ radiation (x-rays).
Detailed MR images allow doctors to examine the body and detect illness.
top of page
What are some common uses of the procedure?
MRI is used to help diagnose a broad range of weather in children due to injury, illness or congenital abnormalities.
When imaging of a child's brain and spinal string is needed, MRI is useful because of its ability to see through the skull and the bones of the skull and spine without radiation. MRI of the brain and spine is used to:
- notice a variety of encephalon conditions and abnormalities like cysts, tumors, bleeding, swelling, or problems with the blood vessels
- discover harm to the brain acquired by an injury or a stroke
- diagnose infectious or autoimmune diseases like encephalopathy or encephalitis
- evaluate issues such as persistent headaches, dizziness, weakness, blurry vision or seizures
- help find certain chronic diseases of the nervous organisation, such every bit multiple sclerosis
- diagnose problems with the pituitary gland and brainstem
- assess the cause of developmental delay
- place and evaluate degenerated or herniated spinal discs
- evaluate the basic of the spine for built or acquired abnormalities
- determine the condition of nervus tissue within the spinal string
In the center, MRI is frequently used in a complementary role to echocardiography (heart ultrasound), computed tomography and catheter angiography to provide information both earlier and after treatment. Cardiac MRI may be used to:
- evaluate the structure of the center and surrounding blood vessels
- assess causes of arrhythmia (abnormal eye rhythm)
- evaluate infections
- assess blood menses to the heart muscle
- evaluate findings following cardiovascular surgery
In the intestinal and pelvic region, MRI is used to:
- diagnose causes of hurting including evaluation for appendicitis
- evaluate for injury after trauma
- diagnose and monitor infectious or inflammatory disorders
- monitor response to cancer treatment
MRI is often the best selection for imaging the joints and bones, where it can assistance:
- diagnose sports-related injuries
- detect the presence of an otherwise hidden tumor or infection in a joint
- diagnose developmental joint abnormalities in children
- find os cancer
- inspect the marrow for leukemia and other diseases
- appraise os loss
- examine circuitous fractures
height of page
How should I prepare my child for the MRI?
Your child may be asked to article of clothing a gown during the exam or allowed to wear their ain wearable if it is loose-plumbing equipment and has no metal fasteners.
Guidelines well-nigh eating and drinking before an MRI exam vary with the specific exam and as well with the imaging facility. Unless y'all are told otherwise, follow your kid'southward regular daily routine and have him/her take food and medications as usual.
Some MRI examinations may require your kid to receive an injection of contrast material into the bloodstream. The radiologist, technologist or a nurse may ask if your child has allergies of any kind, such as an allergy to iodine or x-ray contrast material, drugs, nutrient, or the environment, or if your kid has asthma. The contrast material about commonly used for an MRI test contains a metal called gadolinium. Gadolinium can be used in patients with iodine contrast allergy, just may require pre-medication. It is far less common for a patient to have an allergy to a gadolinium-based contrast agent used for MRI than the iodine-containing contrast for CT. However, even if you know your child has an allergy to the gadolinium dissimilarity, it may still be possible to use it later appropriate pre-medication.
Tell the radiologist if your child has any serious wellness problems or has recently had surgery. Some atmospheric condition, such as severe kidney disease, may foreclose your child from being given gadolinium dissimilarity for an MRI. If your child has a history of kidney disease or liver transplant, it volition be necessary to perform a blood exam to make up one's mind whether the kidneys are performance fairly.
Also, inform your doctor of any recent illnesses or other medical weather condition your child may accept, and if there is a history of heart disease, asthma, diabetes, kidney disease or thyroid problems. Any of these conditions may influence the conclusion on whether dissimilarity material will be given to your kid for the MRI examination.
Jewelry and other accessories should be left at home if possible, or removed prior to the MRI scan. Because they can interfere with the magnetic field of the MRI unit, metal and electronic items are non allowed in the test room. These items include:
- jewelry, watches, credit cards and hearing aids, all of which can be damaged
- pins, hairpins, metallic zippers and similar metallic items, which can distort MRI images
- removable dental work
- pens, pocket knives and eyeglasses
- torso piercings
Tell the technologist if your child has any implanted medical or electronic devices. These objects may interfere with the exam or potentially pose a run a risk, depending on their nature and the forcefulness of the MRI magnet. Many implanted devices will have a pamphlet explaining the MRI risks for that detail device. If you take the pamphlet, it is useful to bring that to the attention of the technologist or scheduler before the exam. Some cochlear implants can be scanned, but at that place are preparations needed. Some implanted devices require a brusk catamenia of time later placement (commonly 6 weeks) before being safe for MRI examinations. Examples include just are not limited to:
- cochlear (ear) implant
- clips used for brain aneurysms
- metal coils placed within claret vessels
- cardiac defibrillators and pacemakers
- artificial heart valves
- implanted drug infusion ports
- artificial limbs or metallic joint prostheses
- implanted nerve stimulators
- metal pins, screws, plates, stents or surgical staples
In general, metallic objects used in orthopedic surgery pose no run a risk during MRI. Withal, a recently placed artificial joint may require the utilise of another imaging procedure. If there is any question of their presence, an x-ray may be taken to detect and identify any metal objects.
Yous should notify the technologist or radiologist of whatsoever shrapnel, bullets, or other pieces of metal which may exist nowadays in your child's torso due to prior accidents. Strange bodies near and especially lodged in the optics are peculiarly of import. Tooth fillings and braces ordinarily are not afflicted by the magnetic field, only they may distort images of the facial area or encephalon, so the radiologist should be enlightened of them.
Anyone accompanying a patient into the exam room must also undergo screening for metallic objects and implanted devices.
If your child has claustrophobia (fear of enclosed spaces) or anxiety, you lot may want to talk to your pediatrician about obtaining a prescription for a balmy allaying prior to the scheduled examination.
Your kid may need to be sedated in lodge to hold still adequately during the procedure. If this is the example, yous will be given instructions for your kid nearly non eating or drinking several hours prior to sedation and the examination. For the condom of your child during the sedation, it is important that yous fully understand and follow any instructions that have been given. After the procedure in that location will be a recovery menstruation from the sedation. Your child will be discharged when the nurses and physicians believe they are sufficiently awake to be safely sent home.
In general, children who take recently been ill will non exist sedated or anesthetized. If this is the case, or if you doubtable your child may exist getting sick, talk to your physician about rescheduling the exam. When scheduling the test for a young child, ask if a child life specialist is available. A child life specialist is trained to make your kid comfortable and less anxious without sedation and will help your child to remain notwithstanding during the examination.
top of folio
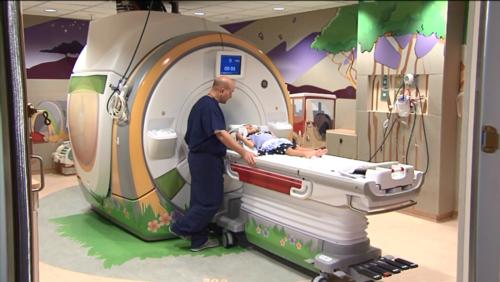
What does the MRI equipment look like?
The traditional MRI unit is a large cylinder-shaped tube surrounded past a circular magnet. Your child will lie on a moveable test table that slides into the center of the magnet.
Some MRI units are designed then that the magnet does not completely surround y'all. Some newer MRI machines have a larger diameter which can be more than comfy for larger size patients or patients with claustrophobia. Other MRI machines are open on the sides (open MRI). Open up units are especially helpful for examining larger patients or those with claustrophobia. Newer open MRI units provide very high quality images for many types of exams; however, older open up MRI units may not provide this aforementioned prototype quality. Certain types of exams cannot exist performed using open up MRI. For more than data, consult your radiologist.
The estimator workstation where the technologist works to ready up the images is located in a dissever room from the scanner.
meridian of page
How does the process work?
Unlike 10-ray and computed tomography (CT) exams, MRI does not employ radiation. Instead, radio waves re-marshal hydrogen atoms that naturally exist within the body. This does not cause whatever chemical changes in the tissues. As the hydrogen atoms return to their usual alignment, they emit different amounts of energy depending on the blazon of tissue they are in. The scanner captures this energy and creates a picture using this data.
In most MRI units, the magnetic field is produced by passing an electric current through wire coils. Other coils are within the machine and, in some cases, are placed around the part of the trunk being imaged. These coils ship and receive radio waves, producing signals that are detected past the machine. The electric current does non come into contact with the patient.
A figurer processes the signals and creates a series of images, each of which shows a thin slice of the body. The radiologist tin study these images from unlike angles.
MRI is often able to tell the difference between diseased tissue and normal tissue better than x-ray, CT, and ultrasound.
top of page
How is the procedure performed?
MRI exams may exist done on an outpatient footing.
Your child will be positioned on the moveable examination table. Straps and bolsters may be used to help your kid stay nonetheless and maintain the correct position during imaging.
The technologist may identify devices that contain coils capable of sending and receiving radio waves around or next to the area of the body under test.
MRI exams by and large include multiple runs (sequences), some of which may concluding several minutes. Each run will create a different set of noises.
If a contrast textile will be used in the MRI exam, a doctor, nurse or technologist will insert an intravenous (Four) catheter, also known equally an IV line, into a vein in your child's hand or arm. A saline solution may be used to inject the contrast fabric. The solution volition drip through the Iv to foreclose blockage of the Four catheter until the contrast material is injected.
Your child will be placed into the magnet of the MRI unit of measurement and the radiologist and technologist will perform the examination while working at a estimator outside of the room.
If your exam uses a dissimilarity material, the technologist will inject it into the intravenous line (IV) afterwards an initial series of scans. They will take more images during or following the injection.
When the examination is complete, yous and your kid may exist asked to look until the technologist or radiologist checks the images in instance boosted images are needed.
Your child'south intravenous line will be removed.
MRI exams generally include multiple runs (sequences), some of which may terminal several minutes.
The doc may likewise perform MR spectroscopy during your examination. MR spectroscopy provides additional information on the chemicals present in the torso's cells. This may add near fifteen minutes to the total exam fourth dimension.
top of page
What will my child experience during and afterward the procedure?
Your child will usually be lonely in the exam room during the MRI process. The technologist volition be able to see, hear and speak with your child at all times using a 2-style intercom. Nonetheless, many MRI centers allow a parent to stay in the room as long as they are also screened for safety in the magnetic environs.
Children will be given appropriately sized earplugs or headphones during the examination. MRI scanners are air-conditioned and well-lit. Music may be played through the headphones to help your child pass the time. Some scanners are equipped with video monitors so that your child may watch a moving picture or TV evidence during the exam.
Information technology is normal for the surface area of your child'south body being imaged to feel slightly warm, just if your child is bothered by the sensation, he/she will be able to talk to the radiologist or technologist through the two-way intercom. It is important that your child remain perfectly nevertheless while the images are existence obtained, which is typically just a few seconds to a few minutes at a time. Your kid volition know when images are existence recorded considering he/she will hear and experience loud tapping or thumping sounds. Your child will exist able to relax between imaging sequences, but volition be asked to maintain his/her position without move as much equally possible.
In some cases, intravenous injection of contrast material may be performed. The intravenous needle may crusade your child some discomfort when it is inserted and your child may experience some bruising. There is also a very small gamble of peel irritation at the site of the Four tube insertion. Some patients may sense a temporary metal taste in their mouth after the contrast injection.
If sedation has not been used, no recovery menstruation is necessary and your child may resume their usual activities and normal diet immediately after the exam. A few patients feel side furnishings from the dissimilarity material, including nausea and local hurting. Very rarely, patients are allergic to the contrast cloth and experience hives, itchy eyes or other reactions. If your child experiences allergic symptoms, a radiologist or other dr. will be bachelor for immediate assistance.
pinnacle of page
Who interprets the results and how practice nosotros get them?
A radiologist, a medico trained to supervise and interpret radiology exams, will analyze the images. The radiologist volition send a signed written report to your main care or referring physician, who will share the results with you.
Follow-up examinations may be necessary, and your doctor will explain the exact reason why some other exam is needed. Sometimes a follow-up exam is done because a suspicious or questionable finding needs clarification with boosted views or a special imaging technique. A follow-upwardly test may as well be necessary and so that whatsoever change in a known abnormality can be monitored over time. Follow-upward examinations are sometimes the all-time way to meet if treatment is working or if an abnormality is stable or inverse over fourth dimension.
top of page
What are the benefits vs. risks?
Benefits
- MRI is a noninvasive imaging technique that does not involve exposure to radiation.
- MR imaging of the soft-tissue structures of the body—such as the centre, liver and many other organs—is more than probable in some instances to identify and accurately characterize diseases than other imaging methods. This detail makes MRI an invaluable tool in early diagnosis and evaluation of many focal lesions and tumors
- MRI has proven valuable in diagnosing a broad range of conditions, including cancer, heart and vascular disease, and muscular and bone abnormalities
- MRI provides a noninvasive alternative to ten-ray, angiography and CT for diagnosing problems of the center and blood vessels
- MRI can detect abnormalities that might be obscured by os with other imaging methods.
- The MRI gadolinium dissimilarity cloth is less likely to cause an allergic reaction than the iodine-based dissimilarity materials used for x-rays and CT scanning.
Risks
- The MRI exam poses almost no hazard to the average patient when advisable safety guidelines are followed.
- If sedation is used, in that location are risks of excessive sedation. Notwithstanding, a nurse or doc monitors your child's vital signs to minimize this adventure.
- Although the strong magnetic field is not harmful in itself, implanted medical devices that contain metal may malfunction or cause problems during an MRI exam.
- Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is currently a recognized, merely rare, complication believed to exist acquired by the injection of gadolinium-based dissimilarity material in patients with very poor kidney part. Screening for acceptable kidney office before because a contrast injection minimizes the risk of this very rare complexity.
- There is a very slight risk of an allergic reaction if contrast textile is injected. Such reactions usually are mild and easily controlled past medication. If you feel allergic symptoms, a radiologist or other physician will be available for immediate assistance.
- After undergoing an MRI examination, modest amounts of gadolinium dissimilarity material may remain in the patient'due south body, including the brain. Gadolinium memory has not been shown to be harmful to patients with normal kidney function, and the do good of an authentic diagnosis far outweighs whatever potential hazard.
top of page
What are the limitations of Pediatric MRI?
High-quality images are bodacious only if your kid is able to remain perfectly still and follow breath-holding instructions while the images are being recorded. If your child is broken-hearted, dislocated or in severe pain, he/she may find information technology difficult to lie notwithstanding during imaging.
A person who is very large may not fit into the opening of certain types of MRI machines.
The presence of an implant or other metallic object sometimes makes information technology difficult to obtain clear images. Patient movement tin can have the same issue.
A very irregular heartbeat may bear upon the quality of images obtained using techniques that time the imaging based on the electrical activity of the heart, such as electrocardiography (ECG).
An MRI exam typically costs more and may accept more time than other imaging exams. Talk to your insurance provider if you have concerns about the toll of MRI.
MRI is generally not recommended for seriously injured patients. However, this decision is based on clinical judgment. This is because traction devices and life support equipment may distort the MR images. As a result, they must be kept away from the area to be imaged. Some trauma patients, however, may need MRI.
top of page
This folio was reviewed on January, 28, 2020
Images
Pediatric Content
Some imaging tests and treatments have special pediatric considerations. The teddy bear denotes child-specific content.
- RadInfo 4 Kids
Sponsored By


Please note
RadiologyInfo.org is not a medical facility. Please contact your medico with specific medical questions or for a referral to a radiologist or other medico. To locate a medical imaging or radiation oncology provider in your community, you lot tin can search the ACR-accredited facilities database.
This website does non provide cost information. The costs for specific medical imaging tests, treatments and procedures may vary by geographic region. Talk over the fees associated with your prescribed procedure with your physician, the medical facility staff and/or your insurance provider to get a better understanding of the possible charges you volition incur.
Web page review procedure: This Web page is reviewed regularly by a md with expertise in the medical surface area presented and is further reviewed past committees from the Radiological Society of N America (RSNA) and the American College of Radiology (ACR), comprising physicians with expertise in several radiologic areas.
Exterior links: For the convenience of our users, RadiologyInfo.org provides links to relevant websites. RadiologyInfo.org, RSNA and ACR are not responsible for the content contained on the web pages found at these links.
Source: https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info/pediatric-mri
0 Response to "What Imaging Can You Not Do on a Baby"
Postar um comentário